How Trauma Affects the Brain
Brain trauma can stem from various causes and may lead to serious physical, cognitive, and emotional effects that persist for months after the incident. While some symptoms appear immediately, others may not surface until days or even weeks later.
Both physical and emotional symptoms from brain trauma can be significant, but treatments are available and early diagnosis can improve your prognosis. Cooper Hurley Injury Lawyers provides information on how trauma affects the brain and what you can do to manage these injuries.
What Is Brain Trauma?
Brain trauma refers to any injury to the brain caused by an external force. It can also refer to emotional trauma that causes brain damage. While physical injury causes damage to the structures of the brain, emotional trauma can inhibit the growth of new brain cells, cause an increase in stress hormones, and affect the way a person responds to fear.
The connection between trauma and the brain is complex. Incidents such as car crashes or acts of violence can result in both physical brain injuries and emotional trauma, often occurring simultaneously. Additionally, structural damage can make it more likely for conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD, to develop.
What Does Trauma Do to the Brain?
Physical brain trauma is also known as a traumatic brain injury (TBI). TBIs can vary in severity from a minor concussion after a fall, to a coma from a wound to the head.
Trauma of all severity levels has the potential to cause brain bruising, swelling, and bleeding. Generally, the more serious the brain injury, the longer it takes to recover. Some effects of TBIs may be lifelong.
The specific effects and long-term impact of a brain injury largely depend on which area of the brain is affected. For instance, damage to the frontal lobe behind the forehead could cause impairments in concentration and judgment.
Know the Symptoms of a Traumatic Brain Injury
Signs of a TBI vary. You may not even notice some symptoms for hours or days following the initial injury. Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Confusion and difficulty speaking
- Nausea and vomiting
- Loss of consciousness
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Persistent headaches

Can Emotional Trauma Cause Brain Damage?
Emotional trauma, like physical trauma, can have a profound effect on different parts of the brain. High levels of stress hormones can reduce the growth of new brain cells and brain connections. Often, this loss of connections is concentrated in the hippocampus, which can change the way your body processes emotions such as fear.
Many events that cause brain trauma, such as car accidents or violent events, can result in both physical and emotional damage. These effects can even amplify each other.
PTSD is common in individuals with brain trauma, and so are other mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression. If you suspect you’re suffering from lingering emotional symptoms after a TBI, seek help.
Recognize the Important Mental Health Symptoms
PTSD and other mental health conditions may not develop until long after your accident. Be gentle with yourself during your recovery and talk to a healthcare provider if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Difficulty sleeping and nightmares
- Avoiding situations associated with your accident
- Feeling numb or detached from the world around you
- Frequently feeling on edge, irritable, or angry
- Mentally reliving your accident
If you or someone else is experiencing a mental health emergency, contact 911.
Common Causes of Brain Trauma
Brain injury cases are complex and can have many different causes. Activities that expose your head to injury—such as sports or home repairs—carry a risk of physical trauma. Likewise, emotionally intense situations or prolonged stress can lead to emotional trauma.
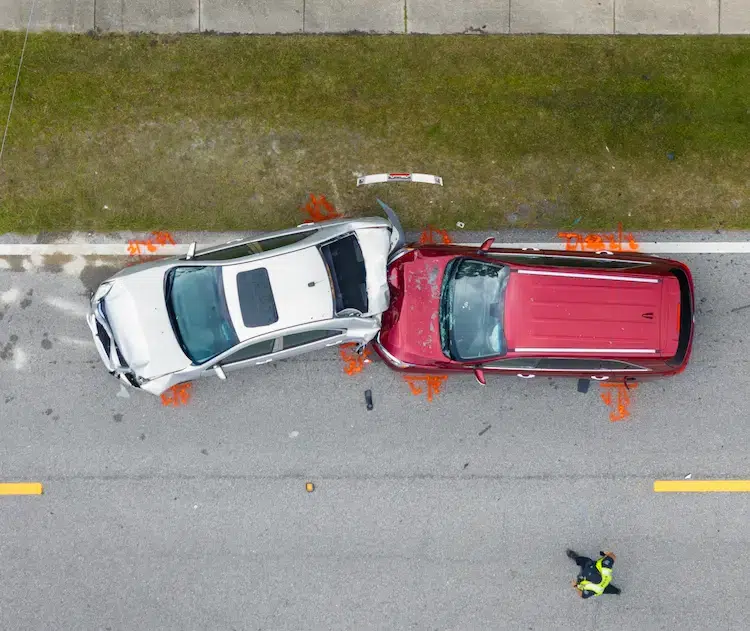
Motor Vehicle Accidents
Over 2.4 million people were injured in traffic crashes in 2023. About 80,000 were on motorcycles, while over 100,000 were on foot or bicycle. No matter how you get around, car accidents and truck accidents put you at risk of brain trauma.
Intense forces in a car crash can cause acceleration-deceleration injuries, where your brain is injured from bouncing inside your skull.
You can prevent brain trauma caused by a traffic crash by following traffic laws, wearing safety gear such as a seat belt or helmet, and making sure your car has up-to-date safety features.


Slip and Falls
In 2022, more than 8.5 million people went to the emergency room with a fall injury. Falls can be dangerous from any height—even tripping on the floor can cause serious injury.
A fall can cause a direct injury to your brain, sometimes called a coup injury. It can also cause a contrecoup injury, which is a contusion on the opposite side of the brain caused by the brain moving backward after an impact.
Other Accidents
Sports injuries are a major cause of brain injuries, especially in children. Sports and recreational activities cause 21 percent of the TBIs in children and adolescents every year and 10 percent of the TBIs in the overall population.
Military members are also at risk for brain trauma. Over 500,000 current and former military members were diagnosed with a TBI between 2000 and the end of 2024. While most diagnosed TBIs were mild, over 10,000 cases were classified as severe or penetrating.
How Brain Trauma Is Diagnosed
Brain trauma is often diagnosed right after an accident, but it can take much longer to identify some cases, especially milder ones. Patients and healthcare providers may not notice some TBI symptoms until days or weeks later. Occasionally, concussions and other injuries don’t show up on scans.
Starting TBI treatment right away is key for protecting your brain. It’s important to get checked out after a hit to your head, even if you feel fine. Your doctor will want to know about the accident and ask questions to determine whether you’re experiencing certain symptoms.
Your doctor will likely recommend a neurological evaluation, and they may also order blood work or imaging such as an MRI or a CAT scan. Obtaining a TBI diagnosis can provide you with both treatment and legal options.
Treatment and Recovery Options
A TBI diagnosis is the first step toward recovery. From addressing physical damage to supporting mental health, a range of treatments can help improve your overall well-being. When it comes to treatment options, knowledge is power. Hospitals, charities, and law firms all provide information on what to do after a TBI.

TBI Treatment
After a serious TBI, doctors may use surgery to remove blood clots, repair skull fractures, or relieve intracranial pressure. These surgeries are often life-saving for patients and are frequently done on an emergency basis.
Your doctor may also prescribe medication after a TBI. Many drugs can treat the immediate symptoms of a TBI, such as diuretics to decrease fluid pressure in the skull or anticoagulants to improve blood flow. Others can help with longer-term effects, such as antidepressants to treat mood swings or anticonvulsants to prevent seizures.
Rehabilitation can help patients adjust to life with a TBI and build back skills that were lost in the injury. Physical, occupational, and speech therapy all take advantage of the brain’s neuroplasticity—its ability to build new connections. Over time, even seriously injured patients can learn to function better within their families and out in the world.
Mental Health Treatment & Support
Mental health treatment is often a large part of a patient’s post-TBI care plan. Cognitive behavioral therapy, or CBT, can help you address the connection between your thoughts and your behavior. Medications can help you better handle symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and intrusive thoughts.
Patients with PTSD may benefit from more specialized therapies such as eye movement desensitization and reprocessing, or EMDR. This therapy can help change how a memory is stored in the brain and thus reduce some negative symptoms. PTSD patients may also benefit from connecting with others in support groups.
If your brain trauma has caused an aversion to a specific activity, place, or thing, you may benefit from exposure therapy. This treatment exposes you to your feared object in a structured way. Over multiple treatments, exposure therapy can help you reduce your negative reaction and build new associations around your fear.
Self-Care Practices
You can support your recovery from a TBI with self-care practices. Many patients find that journaling helps them keep track of their emotions and notice patterns. Others find relaxation and stress reduction with activities such as yoga and meditation.
PTSD and TBI patients can also benefit from a healthy lifestyle with a moderate diet and plenty of sleep.
Financial Considerations for Treatment
Treatment for a TBI can be costly, but there are multiple avenues for funding. You may receive an insurance settlement from the accident or have your health insurance cover some of your medical bills. If the accident happened on the job, you may be eligible for workers’ compensation.
Local fundraising or charitable organizations may be an option for living expenses. You can also pursue benefits such as Social Security Disability Insurance if your TBI leaves you unable to work or VA benefits if your injury is service-related.
Finally, you have the right to pursue legal options for obtaining funds, especially if you cannot reach a reasonable settlement with the insurance company. Depending on the circumstances of your accident, you can file a catastrophic injury lawsuit with a TBI lawyer.
Effects of Brain Trauma on Children
Brain trauma can be especially damaging to children and their developing brains. TBIs often affect a child differently from an adult, even if the same part of the brain is affected. The impacts of an injury can also be much more severe.
What’s more, younger children may struggle to communicate their symptoms, which can make diagnosis more difficult. After an accident, caregivers can watch injured children for signs that they are struggling with their balance, falling behind in school, having more emotional outbursts, or experiencing changes in their sleep patterns.
Because they have weaker neck muscles, children are more likely to experience neck and vertebral damage during TBIs. If you suspect your child has any brain trauma, seek medical care right away.

Supporting Children Experiencing Trauma
There’s no timetable for a child’s recovery from a TBI. Symptoms may linger for weeks and months after the accident. With care and understanding, however, children can often recover.
After a TBI, seek all appropriate medical care for your child. Try to keep a quiet, restful atmosphere at home. Your child may not feel up to doing their normal activities, and doctors may advise steering clear of certain sports and outdoor play.
Seek care for your child’s emotional well-being, too. Therapy can help kids work through the trauma of their accident and make sense of their recovery.
Additional Mental Health Challenges
Even if you don’t have a TBI or develop PTSD, you may still experience mental health challenges stemming from an accident or injury. These may include:
- Stress and anxiety resulting from financial challenges following an accident
- Coping with serious injuries, long-term healing, and disabilities
- Dealing with survivor's guilt if you were in an accident with fatalities
- Fear of driving, or amaxophobia, if you were in a car accident
Any accident or injury can lead to mental health symptoms. If you find yourself struggling, reach out to a trusted loved one or a healthcare professional.
Seeking Compensation for Brain Trauma After an Accident
Brain trauma can have many causes, as well as both physical and emotional consequences. While even mild TBIs can have a long and painful recovery, swift medical treatment can improve your outcomes. Knowing important TBI facts and how trauma affects the brain can help you be prepared in the event of an accident or emergency.
If you’ve recently suffered a brain injury, Cooper Hurley Injury Lawyers is here to assist you in understanding your legal options. You can contact us for a no-obligation consultation.
